In this article, you will find the list of all ADB and Fastboot Commands for Android devices. You can execute these commands on any computer regardless of its operating system (Windows, Mac, or Linux). The commands are universal, which means the same commands will work on any Android device, regardless of its manufacturer or device variant.
Android enthusiasts, familiar with unlocking bootloader, rooting, or installing a custom recovery on their device, must be well aware of ADB and fastboot. These are system utilities that provide backend of Android when it is connected to a computer.

ADB or Android Debug Bridge can be used when an Android phone is connected to PC on fastboot or bootloader mode. There are some specific codes that can be executed using a computer to perform a function on Android devices. Mostly, people use fastboot to unlock the bootloader of a phone. Sometime, you may need to unbrick the device (in case of a hard brick) using fastboot.
Most of the fastboot and ADB commands produce the same results on any device regardless of the manufacturer or variant. If you are stuck somewhere, where you need fastboot / ADB command to assist, this post is for you. I have listed all the important fastboot, and ADB commands in the table given below. Codes, along with its property and functions, are also appropriately mentioned. Use Ctrl + F to find your requirement.
Pre-requisite
Before going to the fastboot & ADB commands, you need certain tools and settings to be enabled on your device as well as the computer. Otherwise, you can not make use of the fastboot or ADB commands. The tools are needed to be installed on the computer. On the other hand, the necessary settings are to be made on the phone.
Methods are the same for all Android smartphones. So, don’t worry about the OEM or variant. Consider the following checkpoints:
- You need to enable USB Debugging mode to connect your Android phone to computer. (Settings > About Phone > Build number > Tap it 7 times to become developer; Settings > Developer Options > USB Debugging).
- Download Android SDK Platform Tools (ADB & Fastboot)
- Mac users: Setup ADB on Mac (using Homebrew)
- USB Cable: Preferably, the one provided by the manufacturer.
- Optional: Download & Install Android USB Driver on your computer.
ADB Commands list
Here is the complete list of all the ADB commands that you can execute using the command prompt or terminal while connecting the Android device to the PC with all required settings. Perform the following if you had fulfilled the prerequisites mentioned above:
adb help | Displays the help documentation on ADB commands |
adb devices | List of all Android devices that are correctly connected to the PC via ADB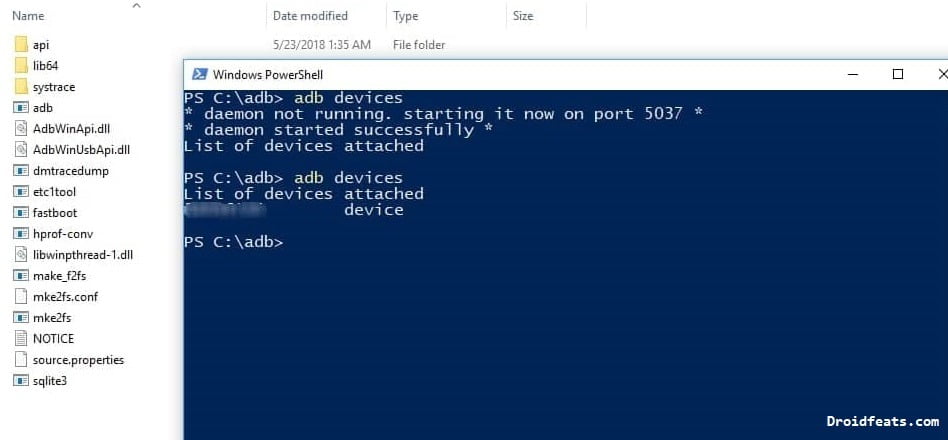 |
adb usb | It will show you all the connected Android device or Emulators connected to your PC using USB |
adb reboot | Restart your Android to system |
adb reboot bootloader | Reboot your device into fastboot or bootloader mode |
adb recovery | Get your Android into recovery mode |
adb sideload ota-update.zip | Used to manually install OTA updates using recovery mode (when the ZIP file is on the computer, not in mobile). Read more about it here! |
adb install | Install APK files manually on your Android using ADB |
adb install filename.apk | Install APK (replacing the file name with the particular APK file name) |
adb install -r filename.apk | Re-install or update an APK to a newer version on Android using ADB |
adb install -s filename.apk | Install APK in the external SD Card (if supported by the application) |
adb uninstall | Uninstall any app using ADB command (see next) |
adb uninstall com.tencent.ig | Uninstall PUBG app package (replace package name with your desired one) |
adb uninstall -k com.tencent.ig | Uninstall the app keeping the data and cache untouched |
adb jdwp | Full list of JDWP (Java Debug Wire Protocol) processes on the Android |
adb bugreport | Check then the dumpsys, dumpstate and logcat data |
adb logcat | Display full log data on the screen |
adb get-serialno | It displays the ADB instance serial number string associated with the device |
adb wait-for-device | It is used to program the device to wait for some time until another process is done |
adb get-state | Shows the device status in the command prompt or terminal |
adb start-server | Starts the ADB server process |
adb kill-server | Terminate the ADB server process |
adb backup // | Using this command, you can create a full backup of your Android device and save it to the computer |
adb restore // | Use this command to restore the backup |
adb connect ip_address_of_device | Using this command, you can connect the IP address of your Android device to the computer. Remember to change the IP address in the code. |
Push and Pull files using ADB
Push and pulls are used to transfer any files from the device to the computer or vice versa. To pull a file from the Android device to the computer, you need to provide the full path of the file. You can use the following ADB command:
adb pull </path/filename>You need to change the file name with an extension. For example, we are pulling a file called “CartoonHD.apk“. You need to execute the command in the following way:
adb pull /system/app/CartoonHD.apkOn the other hand, while pushing files from computer to Android using ADB, you can execute the following command:
adb push <source-path> <target-path>Same as before, you need to provide the full path with extension and the destination path as well. Check out the example below:
adb push /local/path/CartoonHD.apk /sdcard/apps/ADB Shell Commands list
Here is the complete list of all the ADB Shell commands that you can execute using the command prompt or terminal while connecting the Android device to the PC with all required settings.
| ADB Shell Commands | Functions |
|---|---|
adb shell | Starts the remote shell command console in the device and lets you control the Android through it |
adb shell wm density | Use it to change the pixel density of your Android device (details given below) |
adb shell pm list packages | Shows all the installed apps package name on your Android |
adb shell pm list packages -s | Shows the list of all the system apps installed on your Android with the package name |
adb shell pm list packages -3 | List of all the 3rd party apps installed on your Android |
adb shell pm list packages -d | Disabled apps list on your Android |
adb shell pm list packages -e | Enabled (active) apps list on your Android with package names |
adb shell pm list packages -u | List of all the apps that you uninstalled from your Android with installed pages |
adb shellHit enter and execute the following: cd /system | These commands change the directory to /system |
adb shellHit enter and execute the following: rm -f /sdcard/whatsapp.apk | Delete a file: replace whatsapp.apk to your desired file name with extension |
adb shellHit enter and execute the following: rm -d /sdcard/DCIM | Delate a folder: replace DCIM to your desired folder name |
adb shellHit enter and execute the following: mkdir /sdcard/Folder1 | Create a new folder “Folder1” under /sdcard |
adb shellHit enter and execute the following: netstat | Check the network statics on your Android device using ADB |
adb shellHit enter and execute the following: ip -f inet addr show wlan0 | Shows the device’s Wi-Fi IP address |
adb shellHit enter and execute the following:top | Use this Coe to monitor the running CPU process on your Android device |
adb shellHit enter and execute the following:getprop ro.build.version.sdk | Get the property of Android’s build.prop configuration |
adb shellHit enter and execute the following:setprop net.dns1 1.2.3.4 | Use to set the values of built.prop configuration and change the properties |
Uninstall a system app using ADB
If you want to uninstall a system app via ADB Shell command, you can execute the following code:
adb shell pm uninstall -k –user 0 package.name.comReplace package.name.com with the actual package name that you want to uninstall from your Android system. This method is the easiest way to uninstall bloatware which comes inbuilt with the system that can not be uninstalled generally from the app menu. For example, if Facebook comes as a system app, and you want to remove it, execute the code in the following way:
pm uninstall -k --user 0 com.facebook.katanaADB Shell dumpsys command
adb shell dumpsysUsing the dumpsys command, you can gather all the system data about your device’s hardware and software configuration. You can also use it to get information about your Android device’s specific elements, such as the battery, display, and battery stats.
adb shell dumpsys displayadb shell dumpsys batteryadb shell dumpsys batterystatsChanging the Pixel density using ADB Shell
You can easily change the Pixel density of your Android device’s screen using adb shell wm density commands. In order to do that, you need to know the actual Pixel density of your device. Let’s take an example with the Galaxy S9 Plus. At first, you need to know the original resolution executing the adb shell dumpsys command.
Following are the info about phone’s display, resolution, and density for Galaxy S9 Plus (after executing adb shell wm density):
mDisplayInfos=
PhysicalDisplayInfo{1440 x 2960, 60.000004 fps, density 3.5, 530.086 x 529.464 dpiIf you want to set a lower resolution, you can check out the following examples (remember, the values may vary from device to device):
for 1080p (FHD)
adb shell wm size 1080x2220adb shell wm density 480for 720p (HD)
adb shell wm size 720x1560adb shell wm density 350Depending on your device, you can set the values, whichever looks excellent for you.
ADB Shell command to Send SMS screen
With this ADB command, you can send a text message from your Android phone while connected to the computer:
adb shell am start -a android.intent.action.SENDTO -d sms:CCXXXXXXXXXX --es sms_body "SMS BODY GOES HERE" --ez exit_on_sent true
adb shell input keyevent 22
adb shell input keyevent 66ADB Shell for screenshots
Using this code, you can capture a screenshot on your Android phone and pull the snapped screen to your computer instantly:
adb shell screencap /sdcard/screenshot.pngHit enter, and then:
adb pull /sdcard/screenshot.pngScreen recording on Android using ADB Shell command
Android 4.4 Kitkat and above have a shell utility to record the screen and pull the video to the computer. Execute the following commands:
adb shell screenrecord /sdcard/movie.mp4(Press Ctrl+C or Command+C to stop the recording)
adb pull /sdcard/movie.mp4By default, the screen recording is limited to 3 minutes only. If you want to set a condition like clip duration, resolution in pixels, and video bitrate, you can use the following commands:
adb shell screenrecord --size 1920x1080 /sdcard/movie.mp4I used a 1920x1080p resolution here for an example. You can change the value according to your needs.
Next, use the following command to set the video duration:
adb shell screenrecord --time-limit 120 /sdcard/movie.mp4Similarly, you can also set the bitrate of the video output. For example, I am setting the bitrate to 4MBPS. The code would be as follows:
adb shell screenrecord --bit-rate 4000000 /sdcard/movie.mp4ADB Shell commands for copy, move & paste
Execute the following command to copy and paste files/folders:
adb shelland then enter the following:
cp /sdcard/The_Shawshank_Redemption.mp4 /sdcard/Movies(Replace the source file and destination value as per your requirements.)
Next, to move a file or a folder from one location to another, you can execute the following:
mv /sdcard/The_Shawshank_Redemption.mp4 /sdcard/Movies(Replace the source file and destination value as per your requirements.)
To move a file from one location to another with a new name, use the following:
mv /sdcard/facebook.apk /sdcard/facebook-mod.apkADB Shell KeyEvent commands (for advance users)
Using the Shell KeyEvent commands, you can trigger certain functions perform by hardware buttons and UI options on your Android device. Execute these codes only if you know about tweaking VM heap to improve performance.
adb shell input keyevent 3 // Home btn
adb shell input keyevent 4 // Back btn
adb shell input keyevent 5 // Call
adb shell input keyevent 6 // End call
adb shell input keyevent 26 // Turn Android device ON and OFF. It will toggle device to on/off status.
adb shell input keyevent 27 // Camera
adb shell input keyevent 64 // Open browser
adb shell input keyevent 66 // Enter
adb shell input keyevent 67 // Delete (backspace)
adb shell input keyevent 207 // Contacts
adb shell input keyevent 220 / 221 // Brightness down/up
adb shell input keyevent 277 / 278 /279 // Cut/Copy/PasteFastboot Commands list
Here is the complete list of all the fastboot commands that you can execute using the command prompt or terminal while connecting the Android device to the PC with all required settings. Perform the following if you had fulfilled the prerequisites mentioned above:
| Fastboot commands | Functions |
|---|---|
fastboot devices | Executing this command will show you the list of Android devices connected to the PC on Fastboot Mode.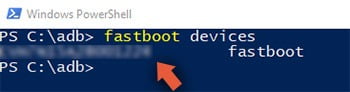 |
fastboot oem unlock | With this code, you can unlock the Bootloader of your Android device (if OEM permits). There is a detailed guide for MediaTek users on our site: check out here! Or Browse bootloader unlocking guide for your device here! |
fastboot oem lock | Relock the bootloader if you want to go back to stock position on your Android device |
fastboot reboot bootloader | Reboot the device into Fastboot Mode again from the Fastboot Mode itself. (necessary sometimes while flashing some image files) |
fastboot flash | This is the most important command for Android enthusiasts. Using this command, you can flash anything to your Android, like an OTA ZIP or a TWRP Image. |
fastboot flash boot boot.img | Use to flash boot image on your Android. For example: flashing a Magisk Patched Boot image to root your phone.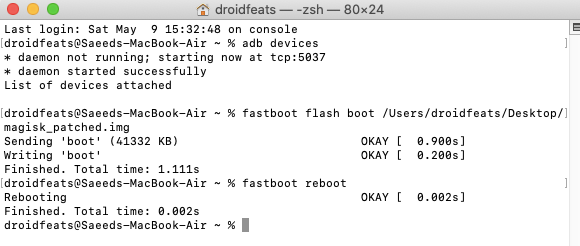 |
fastboot flash recovery recovery.img | Use to flash recovery images like TWRP on Android devices. Read more about flashing TWRP recovery here! |
fastboot boot filename.img | This command is used to boot your device using a particular image file without flashing it. This can be useful for testing purposes before a permanent flash. Read mode! |
Anything left?
So, that’s pretty much on our blog for fastboot, and ADB commands. If I missed anything, please do let me know in the comment section below. I hope this post is helpful for you to perform a plethora of commands using cmd or terminal. If you have any questions about ADB or fastboot controls, do let me know by dropping a comment below. I will reply you back as soon as possible.
Like this post? Please do share the post link on social media to thank me 🙂





6 Comments
Good write up! I’m trying to remove knox restrictions. I’ve tried commands from other sites but command prompt wasn’t happy with the ones I’ve tried. Any help would be appreciated. This is on a Samsung SM-T350.
‘df -h’ commands you did not show.
Thanks for the suggestion. We will update it soon.
I want to set the refresh rate on iqoo 7 legened alway on 90hz using adb shell
ADB and Fastboot are utilities that unlock access to the Android system while your phone is connected to a desktop computer via a USB cable. The computer and cable are integral to this—there’s no app version, and while you can use ADB wirelessly, it’s much more complicated to set up
You are absolutely right that these utilities are essential for unlocking access to the Android system, and that connecting your phone to a desktop computer via a USB cable is necessary for their use. While it is possible to use ADB wirelessly, the setup can be complex and may not be worth the effort for some users. I appreciate your insights on this topic and hope that my post has helped to clarify any questions you may have had about ADB and Fastboot.